Fats are essential to health. They are required for proper cell function, production of hormones, healthy stress response, immunity, detoxification, smooth digestion, and fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. Around 60% of the brain consists of fat. Some of the signs of having insufficient fats or fat malabsorption include:
dry and flaky skin
dandruff (can also be fungal)
dry eye
constipation
poor bile flow and / or gall stones
mood disorders, depression
general inflammation
pain (e.g. arthritis or chronic back pain)
metabolic imbalance (blood sugar imbalance, high triglicerides, low HDL cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol)
Trust biochemistry, not marketing
Don’t skip this paragraph because it will help you make informed decisions.
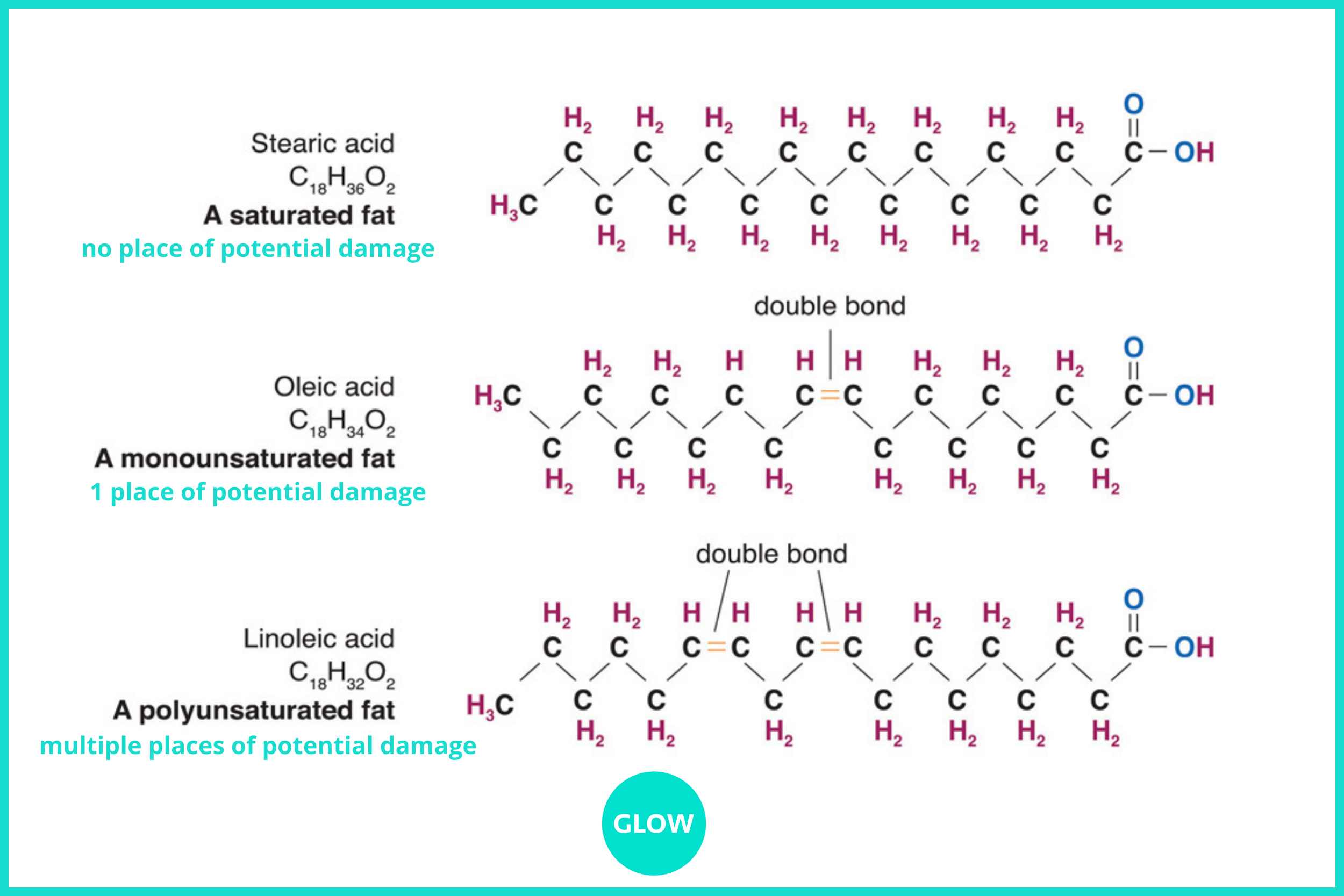
The main differentiating factor between fatty acids is the presence or absence of double bonds between carbon atoms. In chemistry, double bonds are a site of oxidation - the place of potential damage. In other words, the more double bonds in a fatty acid, the more damaged it can become. In the world of nutrition, oxidised fats together with processed sugar are number 1 thing to avoid due to their inflammatory properties.
Oxidation stability is the most important aspect when determining what fat to cook with, no matter what the industry tries to sell. Some fats have a high smoke point but are easily oxidised. It means that they taste better when exposed to a higher temperature but might become toxic when heated, e.g. refined sunflower seed and rapeseed oil. And the other way round - some fats have a lower smoke point but are more resistant to oxidation. Ethical refining of oils increases their smoke point but it only makes sense for fats which are resistant to oxidation, like coconut oil.
Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated fats: each atom of carbon is saturated with hydrogen due to the absence of double bonds, making the fat solid at room temperature and resistant to oxidation. In the body, saturated fats provide stability and integrity to cell membranes so that cell insides don’t spill out, and protect fragile unsaturated fats from damage. Examples: animal fats, butter and ghee, coconut oil and dairy.
Note: If you have cholesterol or metabolic issues like excess weight or insulin resistance, some sources of saturated fats should not be combined with starchy foods. For example, instead of putting butter on toast, use olive oil. Some people may notice best results from stopping starches altogether rather than reducing fat intake. This is why the ketogenic diet works well for some to improve metabolism and lipid panel. Read my post on cholesterol here.
Unsaturated fats: contain atoms of carbon that are not saturated with hydrogen due to the presence of double bonds so are liquid at room temperature and prone to oxidation. In the body, they maintain cell membrane fluidity so that things can get in and out of cells. Monounsaturated fats have one double bond, meaning there is only one place of potential damage. Examples: olive oil, avocado oil (sources of omega 9). Polyunsaturated fats have multiple double bonds so are much more prone to damage and should not be heated. Examples: nut, seed and supplemental oils (sources of omega 3 and / or 6).
All fats that occur in nature are a combination of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids but one type always dominates. For example, olive oil is 18% saturated. Intuitively, cells require both in order to function well. The key is to provide them in appropriate (and unprocessed) ways.
Fats suitable for cooking - resistant to oxidation
Clarified butter and ghee
Butter: ok for baking or cooking eggs; enjoy melted over cooked vegetables
Non-extra virgin olive oil and avocado oil; also good for making mayonnaise and alioli due to the more neutral taste compared with extra virgin counterparts. In my view, avocado oil is too expensive to cook with
Refined coconut oil which has a neutral taste. It should be mechanically or steam refined, like this one or this one
Animal fats: duck and goose fat, lard, beef tallow, drippings
Fats suitable for cold use - prone to oxidation
Rich in polyphenols which act as antioxidants so it’s important to treat them with care - keep away from excess light and heat. Some of these are polyunsaturated fats and for that reason alone should not be heated.
Extra virgin, cold pressed olive oil: use in salad dressings or over cooked vegetables
Extra virgin, cold pressed coconut oil: use in smoothies, energy balls, bulletproof coffee, green tea, or for therapeutic purposes (off the spoon as appetite suppressant, topically for sun burns and anti-fungal properties)
Flax oil: use in salad dressings, smoothies or take it off the spoon as a supplement; keep in a dark bottle in the fridge (polyunsaturated)
All other nut and seed oils like sunflower seed, rapeseed, sesame, peanut, hemp, milk thistle or black seed. They should always be cold pressed and kept in the fridge (polyunsaturated)
Fats to avoid
Regular sunflower seed and rapeseed oils (non-cold pressed, sold in most shops and marketed as suitable for cooking)
Corn and vegetable oils
Liquid coconut oil
Artificial trans fats and all foods that contain them: margarine, vegetable shortening, frozen pizza, shop bought baked foods like croissants and doughnuts and cookies, refrigerated or frozen dough (puff pastry, shortcrust, rolls)
Supplemental oils
The body can make most fats except for two: omega 3 and 6. They are called essential fatty acids, meaning they must come from food or supplements. Omega 3 fatty acids are anti-inflammatory whereas omega 6 can either be either anti- or pro-inflammatory. For optimal health, appropriate balance of omega 6 to 3 should be maintained. Supplements on their own don’t warrant the overall balance but can help, especially when you don’t eat enough food sources on a regular basis.
Fish oil: obtained from the flesh of fish and taken mostly for anti-inflammatory omega 3 fatty acids called DHA and EPA which plant based oils don’t provide. Plant based omega 3 (called ALA), for example from flax, can be converted into EPA and DHA but the process is inefficient and blocked by artificial trans fats and hyperinsulinemia.
Krill oil: contains more antioxidants than fish oil and the body may utilise it even better than fish oil. It is, however, a lot more expensive.
Cod liver oil: obtained from cod livers. Since the liver stores fat soluble nutrients, cod liver oil is taken for active vitamin A (retinol, not beta carotene), some vitamin D, and also omega 3 fatty acids.
Algae based oils: the best option for vegans as they contain DHA and EPA.
Evening primrose, borage, blackcurrant seed oils: provide anti-inflammatory omega 6 fatty acid called GLA. I usually recommend GLA on top of omega 3 in certain health conditions like autoimmunity, chronic pain or hormonal imbalance in females.
Black seed oil (nigella seed): fantastic for people with any atopic condition including asthma, allergies and eczema. Also a great digestive tonic. It has a very strong so capsules might be more convenient.
MCT: medium chain triglycerides obtained from coconut that don’t require much digestion, therefore serve as immediate source of energy. Those who are on the low carb or keto diet notice most benefits of taking MCT, for example in coffee or keto smoothies. Good option for epilepsy.
Mixed oils: Udo’s oil is my favourite broad spectrum plant based oil. It contains flax, evening primrose, sunflower seed, coconut, sesame, rice bran, oat bran oils and non-gmo soy lecithin. There is also a version with added DHA from algae.
Summary
Your health should always dictate which fats are the best to use and in what combination with other foods. For example, coconut oil may be great but can contribute to acne in some individuals.
Culinary fats and supplemental oils complement rather than substitute each other and if possible, it’s good to have a variety and use them in different ways. For example, I scramble eggs and make Indian curries with ghee, cook Thai curries with coconut oil, use olive oil in salad dressings, drizzle stir fries with sesame oil and make potato fries with lard or duck fat. My personal regime for supplementing oils is 1 teaspoon of cod liver oil, 1 teaspoons of fish oil twice daily and 1 table spoon of Udo’s oil twice daily.
In the previous post I discussed how to take the most common supplements including supplemental oils, in order to get most benefits.